Since the resumption of the issuance of the national debt by the Ministry of Finance of China in the 1980s, China’s bond market has undergone more than 30 years of hardening and testing, and the achievements have been tremendous. Not only has it played a major role in the domestic economic construction, but after becoming a member of the Asian Bond Market Initiative, it has also played a positive role in the rapid development of the Asian bond market and in responding to the impact of the financial crisis and achieving regional economic recovery.
However, compared with developed countries, China’s bond market still has some gaps, mainly in terms of small scale, few varieties, imperfect market system, single market participants, slow bond liquidity, and imperfect related systems. As an important part of the Asian bond market, the sustained development and gradual opening of China’s bond market is not only an inevitable requirement for the deepening of the financial market system but also a consistent development direction of the Chinese government and relevant departments.
In terms of bond financing, China can study and promote more international financial institutions to issue RMB bonds domestically or foreign currency bonds issued by domestic and overseas institutions. Therefore, the development of Sukuk will have an inestimable positive effect on the economic construction of China itself, Asia and the world. Specifically, China can accelerate the gradual entry of qualified Islamic financial institutions into the domestic bond market, and at the same time also enter the financial bond market in the Islamic world. This will not only help enrich the main market participants in China but also increase the breadth and depth of the development of the domestic bond market.
At present, China’s bond issuance is mostly guaranteed by the credit and assets of the issuing entity, which naturally sets up obstacles for SMEs to issue bonds. Relatively speaking, Sukuk is more concerned about the reliability of the project assets than the creditworthiness of the issuer. First, by introducing Sukuk, the scope and types of issuers can be expanded, and also the size of China’s securities market. Second, the innovation of the issuance mode can enhance the liquidity and efficiency of internal funds in the bond market. Finally, strengthening the ties between the currency and the capital market can improve China’s bond maturity structure.
The construction of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) can promote bilateral and multilateral economic cooperation and also increase China’s international influence, which will have traction on investment hot spots. The construction and development of the BRI are inseparable from the financing operation of the capital market. The development of Sukuk will have a huge boost to China’s capital market, because of the priority participants in the BRI and their hubs as well as most of the countries in the “two corridors and one area” are Islamic countries. In the capital markets of these countries, Sukuk has played an important role in its economic construction in recent years.
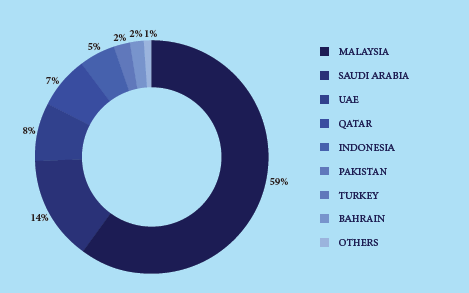
According to the statistics of Allalah Consulting, as of the end of 2013, the total issued amount of Sukuk has reached USD270 billion, of which Malaysia accounted for 59%, ranked first in the market, Saudi Arabia 14%, United Arab Emirates 8%, Qatar 7% Indonesia 5%, Pakistan, Turkey and Bahrain each accounted for 2%, and other countries overall accounted for about 1%. At the same time, in the BRI strategy, these countries will play an indispensable link to connect with other relevant countries.
Furthermore, among the eight-member states of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), five are Islamic countries, namely Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan. China has become the main trading partner of these countries. While among the organisation’s observer states and dialogue partners, Iran, Afghanistan and Turkey are all Islamic countries. At present, many Islamic countries have taken a step forward in developing Islamic financial business, and gradually formed a dual financial system, that is, the situation where Islamic and conventional financial systems coexist. In view of the growing trend of the Islamic financial market in recent years, the four Central Asian countries are also actively working to build domestic Islamic financial centres to attract more investment and financing. Therefore, as a leader of the SCO, China already has the prerequisites for the development of Sukuk and even the Islamic financial market as a whole.
Wafee Yeung is the Managing Director of Allalah Consulting Limited (http://www.allalah.com), the leading Islamic finance advisory firm, based in Mainland China and Hong Kong. He is a qualified accountant and certified tax advisor, possessing over 20 years of practical experience on international tax management, project finance, Islamic finance and Halal businesses. He can be contacted at wafee@allalah.com.




