A Shari’a Analysis And Their Applications In Islamic Finance
Virtual currencies and blockchain have dominated headlines with many citing them as heart of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. In the words of Klaus Schwab, Founder and Executive Chairman, World Economic Forum, “One of the main features of the Fourth Industrial Revolution is that it does not change what we are doing, it changes us.” Undeniably, the impact of these new technologies is affecting economies and industries dramatically. The advent of Bitcoin, for example, reveals how antiquated the banking system and fiat money are. Despite the recent spike in Bitcoin’s media coverage, it would appear that the majority of people are still unfamiliar with bitcoin and blockchain.
What is Bitcoin and Blockchain Technology?
Cryptocurrency is also termed as virtual currency or digital currency. It may be defined as a digital representation of value which does not have legal tender. It is distinguished from fiat currency, which is the coin and paper money of any country and different from e-money, which is a digital transfer mechanism for fiat currency.Bitcoin is one of the types of currencies which is the first and the most famous cryptocurrencies in the world. Bitcoin has little differences from other cryptocurrencies. Therefore, both bitcoin and cryptocurrencies shall be used alternatively in this article.
Bitcoin was invented and developed by Satoshi Nakamoto in the year 2009. It is considered to be a type of crypto or virtual currency, which is generated through a mechanism called cryptography that runs on a software named blockchain. Cryptography is the practice of creating algorithms designed on difficult computational assumptions. Blockchain is a decentralised distributed ledger stored on the computer. It records the transaction chronologically and publicly which allows each individual user to verify the validity of individual transactions and the system. In basic financial terms, we can say that, the blockchain allows anyone to send money from anywhere in the world at minimal cost, without the involvement of central authority such as the central bank or government. This means that bitcoin is not a trusted legal tender as it is not under the control of any central legal authority (government/central bank) nor it can it be minted.
There is no centralised clearing house etc to verify crypto transactions. In more simple words, the blockchain is an open forum for users to see a record of all the exchanges and interactions between users that took place through it which consists of a peer-to-peer network comprised of computers. Blockchain transfers power in the hands of users allowing all users to see the data. Each block in the blockchain has a header, which contains a reference to the previous block, information relating to all the transactions in the block and data related to the mining operation. Bitcoin, is created through the process of mining.
Blockchain in an infinite state machine is a system that has a starting state but no ending state. The state in a blockchain is given by the number of blocks it holds at any moment of time. A change of state, state transition, takes place when a new block is added to the blockchain through a process called consensus. Blockchain links a new state with old states by using cryptography resulting into a single chain which cannot be modified. Bitcoin uses C++ programming language and comprises of around 70 set of commands, which makes it difficult to hack.
The transactions appear in public ledger within minutes.
The European Central Bank describes cryptocurrencies (Virtual Currencies) as “digital representation of value that is neither issued by a central bank or public authority nor necessarily attached to fiat currencies, but is used as a means of exchange and can be transferred, stored or traded electronically. In contrast to fiat currencies, virtual currencies are not legal tender but are nevertheless accepted by members within a virtual community as a medium of exchange and as a unit of account. Virtual currencies must also be distinguished from electronic money such
as PayPal or Ven. In electronic money schemes the link between the electronic money and fiat currency is guaranteed through some legal foundation and funds are shown in the same unit of account (U.S. dollar, Euro, etc.)

Money has no intrinsic value but acts only as medium of exchange and store of value
Are Bitcoin and Similar Currencies Acceptable under Shari’a Guidelines?
Money or currency is neither halal – permissible – nor haram – impermissible. If money is gained or transacted in a lawful manner then it is halal and vice versa. Islam considers money primarily as a medium of exchange to facilitate transactions and not a commodity. As such, the price of this money (interest) must be zero. What does economic experts and Islamic jurists say about money and currency?
Economists have categorised money in the following types:
- Commodity Money: has an inner physical monetary value as well as material substance like gold, silver, salt, etc.
- Fiat Money: does not have an inner physical monetary value but an external monetary value is given by governments or central banks. An example of fiat money is paper money.
- Fiduciary Money: value depends on confidence that it is an accepted medium of exchange. The issuer of fiduciary money promises to exchange it back for a money if requested by the holder. Examples of fiduciary money include cheques, drafts, etc.
- Electronic Money: It represents the actual fiat money but realised in electronic systems. The money can be transmitted via internet etc. Examples of electronic money include debit, charge and credit cards.
Islamic jurists, on the other hand, define money as follows:
- Natural Money: Money created to serve as a medium of exchange and naturally possesses internal physical monetary value. Gold and silver are natural money.
- Commodity Money: possesses internal physical monetary value but lacks the capacity to be used as medium of exchange. This lacking is due to nature of commodities like commodities can perish, expires, or may need extra space of storage etc. Salt, tangible things, grains etc. However, in certain adverse situations like wars, unrest etc, such commodities can also be used as medium of exchange which is due to their internal physical monetary value.
- Fiat Money: does not possess internal physical monetary value but attains an external monetary value by law of the land (government/central bank). Since it does not possess internal physical monetary value, the value of fiat money is derived from the relationship between supply and demand forces. The government declares fiat money to be legal tender, which requires all people and firms within the country to accept it as a means of payment.
Shari’a Viewpoints on Money/ Currency
Ibn Taymiyyah states that the Shari’a has not defined currency specifically, rather it is left to the custom and understanding of the people. Imam Abu Hanifa and Imam Abu Yusuf were of the view that a commodity can be considered as money upon the agreement of only the two transacting parties. However, Imam Muhammad considered commodity as money when there is substantial and widespread acceptance is present. Mufti Taqi Usmani opined that government by legislation can also declare something as money like paper money since government view is widely accepted.
According to Imam Ibn al-Qayyim, when money begins to be treated as a commodity and becomes the objective of transactions, the entire economic system will be in crisis. As per
Shari’a, money is not a commodity, therefore reward of money is contingent on the result of production from productive activity.
According to Islamic economic principles, money has no intrinsic value but acts only as medium of exchange and store of value. From my own point of view, money in itself is neither permissible nor impermissible. It is how money is used and raised. If money is earned and transacted in a lawful manner then it is halal and vice versa.
As per Shari’a, money is not a commodity, therefore, reward of money is contingent on the result of production from productive activity.
When Is Bitcoin Shari’a Permissible?
The main issues surrounding bitcoin or other Current Shari’a viewpoint regarding currency states that it should have widespread acceptance. But governments can also declare something as legal tender. Since Bitcoin does not meet this criteria, Bitcoin or cryptocurrencies should either be straightaway rejected or to be accepted under some guidelines. Given that Shari’a is very robust to act upon innovation, one should assume that there must be some solution to this in the era of technology.
We have witnessed a continuous change in the currency, i.e from barter goods to gold and silver to fiat currency to electronic money and now digital currency as the concept of money evolved across time. Goods, gold, silver, banknotes, electronic money have all played the role of money. With all the boom of Bitcoin, the very essence of Bitcoin is still obscure. While bitcoin in itself is not made illegal in many countries, its status as money varies depending on the jurisdictions’ regulations surrounding its usage. For example, countries such as Japan and the Philippines have officially legalised bitcoin as a digital payment system. Bitcoin or cryptocurrencies do not meet the condition of widespread or legal acceptance of currency due to the fact that they are still in the infancy stage. However, with the passage of time, there is a possibility that it will achieve widespread acceptance and might be accepted by governments as a legal tender.
I am of the view that bitcoin has an external monetary physical value, like fiat currencies, and it can also serve as a medium of exchange, which is a requirement for a currency. If we take the views of Imam Abu Hanifa and Imam Yousuf where a commodity can be considered as currency upon the agreement of only the two transacting parties, and apply the same ruling to bitcoin; then bitcoin can be accepted as a currency since it is accepted by both parties and it is also acting as a medium of exchange.
Islamic banks should consider bitcoin under fiduciary currency rulings (which I name this as fiduciary bitcoin) where the banks can promise to exchange it back for a fiat money or bitcoin if requested by the holder. This is not guaranteeing of money but rather it is the security of money in case of any mishap as well as to provide some legal acceptance to consider it as currency.
When Bitcoin Is Not Shari’a Permissible?
The power to create is in the hands of people who can do anything at any point of time. There are also possibilities that due to disruption to the systems and hardware malfunction which provide the power and storage space to Bitcoin, these disruptions can result in losses for bitcoin holders as they are not secured by any central authority. This is extreme uncertainty.
Moreover, Bitcoin is not backed or based on some economic activity. Rather there is a huge difference between the actual value and market value of bitcoin. The volatility has only increased speculation resulting in Bitcoin investors to hoard and hold Bitcoin instead of spending it. Since investments in bitcoin and cryptocurrency are not linked to the real economy, they thus fail to promote real growth of an economy. Hence, Investing in bitcoin does not benefit the society nor the real economy; nor does bitcoin investments boost services, labour or the production of goods.
Bitcoin is used for speculation and appears to be gambling instead of using as a currency and medium of exchange. This uncertainty, speculation and gambling elements make bitcoin-related investments as Shari’a prohibited.

The Application of Bitcoin or Similar Currencies in Islamic Banking
The world is witnessing huge involvement of technology in the banking industry and blockchain is said to poses the biggest threat to the financial industry. Therefore, Islamic banks should also consider blockchain technology for their daily affairs. Below are some of my suggestions on how bitcoin and blockchain can be applied in Islamic banking.
Islamic banks should work towards making cryptocurrencies as fiduciary cryptocurrencies, which simply means people having trust on the currency. This fiduciary idea will be a new era as bitcoin needs to be accepted (which is possible under fiduciary guidelines) to be considered as currency as well as medium of exchange. However, before this can happen, we must ensure that the value of bitcoin and other currencies become stable and attain market value so as to avoid losses to the Islamic banking industry.
Islamic banks should leverage on the application of the blockchain technology.
The use of blockchain in Islamic banking will primarily affect the way payments, remittances and trading activities are conducted including significantly reducing transaction processing time as well as reducing the costs for providers and transaction fees for consumers. Blockchain also facilitate smart contracts, a digitally coded contracts. Blockchain smart contracts can help automate the contractual processes for Islamic banks as they can mitigate operational risks arising from settlement and counterparty risks.
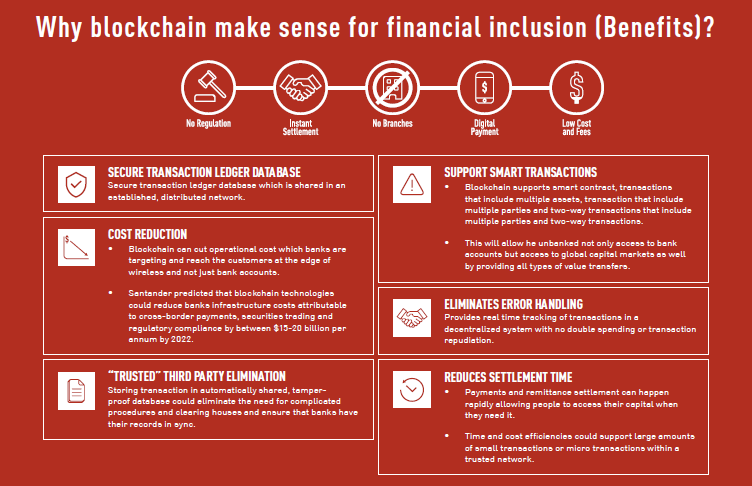
Islamic banks can also use blockchain technology to foster financial inclusion. Blockchain technology is set to make efforts to increase financial inclusion faster and more effective. As a decentralized way of verifying and recording transactions, blockchain overcomes the problem of scaling across borders, and by cutting out the need for intermediaries, it significantly reduces overheads. Thus, through greater speed and efficiency in making payments and transfer-particularly across borders, blockchain ultimately promotes financial inclusion.